
Nursing Times 117: 4, 56-59.Īuthor: Hilary Harkin is ear, nose and throat clinical nurse specialist, Ear, Nose and Throat Outpatient Department, Guyâs and St Thomasâ NHS Foundation Trust. Objective: To investigate associations between age, external auditory canal (EAC) dimensions, and cerumen retention/impaction among persons with Down syndrome (DS). Revisions: 43 formatlistbulleted Contents add The ear can be divided into three parts external, middle and inner. Patients with EACC typically present with otorrhea and a chronic, dull pain due to the local invasion of squamous tissue into the bony EAC ( 2 ). Nurses may be caring for patients with chronic ear problems across many nursing specialties in both hospital and community settings, and they need to understand the structure and function of the ear.Ĭitation: Harkin H (2021) The structure and function of the ear and its role in hearing and balance. External auditory canal (EAC) cholesteatoma (EACC) is a rare entity with an estimated occurrence of one in 1000 new patients at otolaryngology clinics.

Ear problems can be debilitating for patients and may also be associated with other health conditions. The differential diagnosis of lesions in the external auditory canal, however, should not be limited to those benign processes discussed here, but should also include infectious. The ears provide the important functions of hearing and balance. Benign mass lesions of the external auditory canal, such as exostoses and osteomas, are common findings on physical examination but most often do not require treatment. The EAC is easily delineated, measuring 2.5 cm in length, extending from the external auditory meatus to the tympanic membrane. This article comes with a self-assessment enabling you to test your knowledge after reading it An outside person who measures and reports on the state of a persons or business finances. The external auditory canal develops from the first ectodermal brachial groove, between the first (mandible) and the second (hyoid) branchial arches.
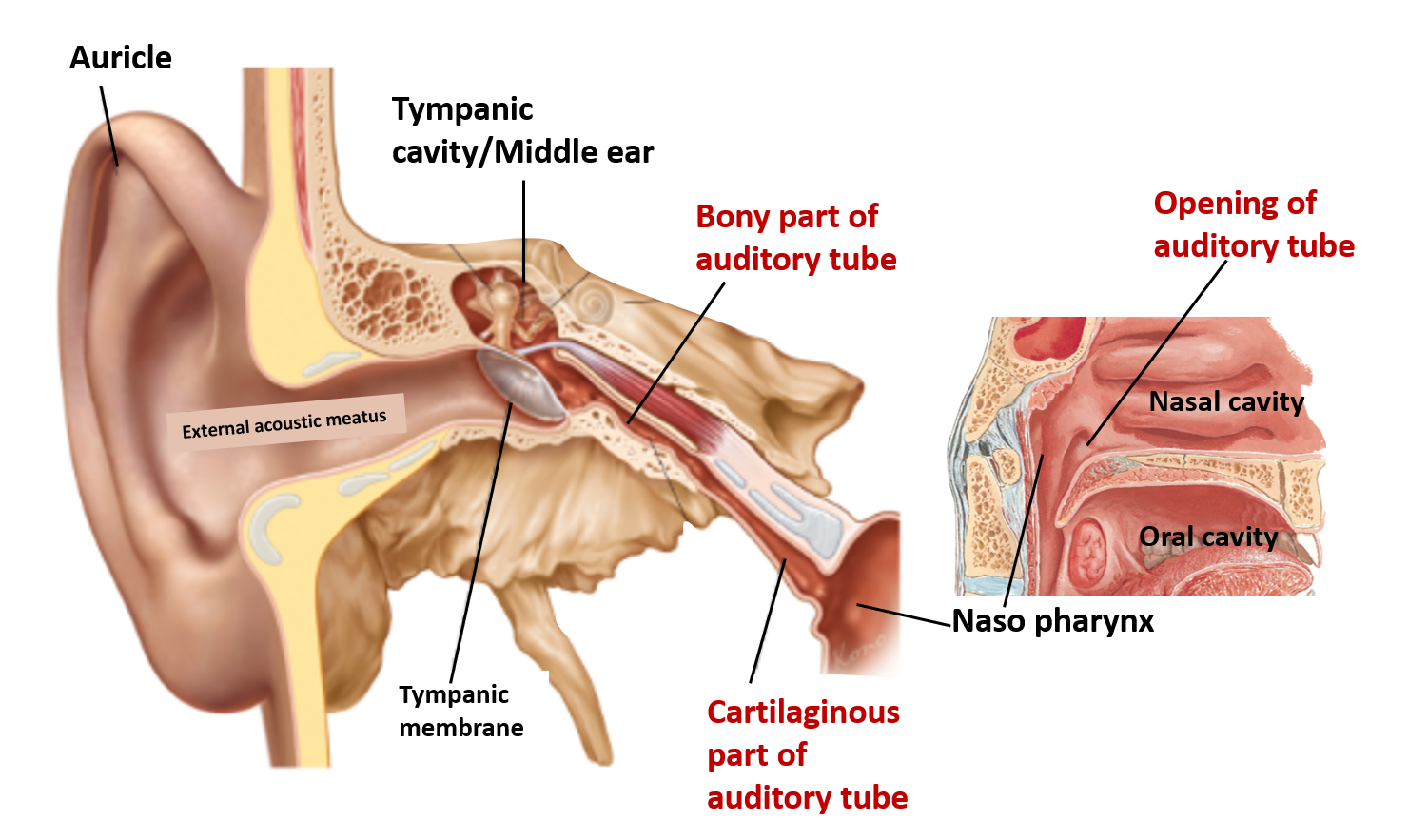
Nurses need to understand the structure and function of the ear as they may be caring for patients with chronic ear problems across many specialities in hospital and the community. The Eustachian tube is formed from the proximal portion of the tubotympanic sulcus.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
