
#PILON FRACTURE ORIF CPT FULL#
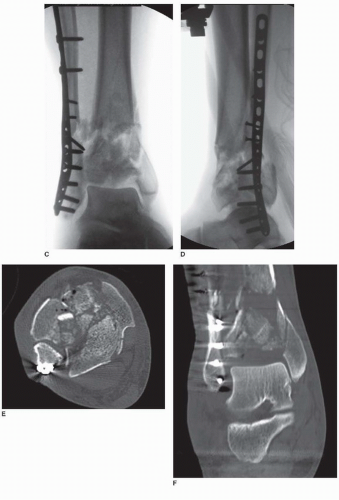
The patients were allowed for full weight bearing ambulation after complete union. Partial weight bearing was allowed when the callus formation was observed on X-rays. VAS score and AOFAS score were detected at the final follow-up. Clinical and radiographic examinations were performed at 4 weeks, 2, 3, 6 and 9 months post-surgery. Patients were examined clinically at 2 weeks after discharge. Tibial metaphyseal comminution was also fixed using medial distal tibial anatomical locking plate and lateral plates if necessary.Īostoperative xray after defenitive fixationĪfter the surgery, identical rehabilitation protocol was started for patients in both groups. The distal articular surface of the tibia was reduced through anteromedial approach. The definite treatment (ORIF) was performed after one to two weeks when the soft tissue inflammation resolved. Patients were discharged from hospital 24 to 48 hours after first stage surgery according to patients clinical examination. In the two-stage group, the fracture was fixated using a delta frame external fixator along with fibula fixation within 24 hours after the accident.
The patients in the PORIF group underwent surgery within the first 24 hours after the accident using anteromedial approach, medial distal anatomical plate and additional lateral plates if necessary for Pilon fractures and one-third tubular plates for fibula fracture. Research process confirmed by Taleghani Hospital ethics committee board. After the usual preoperative clinical and radiological examination (CT scanning and X-rays), eligible patients were asked to sign the informed consent. Primary ORIF was performed on 21 patients by the first author and the two-stage treatment was used by the second author. Among them, 10 patients were excluded due to the open fractures (2 patients), rheumatoid arthritis (2 patients), concomitant fracture in the lower limb (2 patients), severe soft tissue damage (Tscherne grade 3) (2 patients), varicose vein (one patient), and compartment syndrome (one patient). In a retrospective study, all patients admitted with diagnosis of Pilon farcture (AO/ OTA type 43.C) in Taleghani Hospital (Affiliated with Shaheed Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran) between 20 were reviewed. In current prospective study, we aimed to compare the clinical, functional and radiologic outcomes and the rate of soft tissue complications in treatment of Pilon fractures with PORIF and two-stage approaches. There are limited studies comparing the outcomes of primary ORIF (PORIF) and two stage approaches in treatment of Pilon fractures resulted in conflicting outcomes ( 14). These complications have been reported even for minimally invasive treatment of Pilon fractures ( 29). This may necessitate several surgeries and even amputation ( 24- 28). However, once the soft tissue is severely injured, the patient must be hospitalized for a long time because of delayed wound healing and superficial or deep infection. For these reasons, some surgeons prefer to perform early primary ORIF, which was associated with good outcomes, especially in less severe fractures ( 22- 24). A major drawbacks of this method is its long-term hospital stay and increased risk of infection and lack of anatomical reduction due to delayed operation ( 14, 19- 21). Numerous investigators have suggested the two-stage approach including primary fixation with EF followed by definite internal fixation after soft tissue healing is the most commonly used treatment for these injuries, especially for AO/OTA type C Pilon fractures ( 15- 18). In addition to controversies about the most superior treatment option, the appropriate time for treatment of Pilon fractures is also conflicting ( 14).
Several options, having various advantages and disadvantages, have been introduced for the treatment of Pilon fractures including close reduction and casting, combined intramedullary nailing and plate fixation, open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF), minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis, external fixation (EF), the two-stage treatment with EF and ORIF ( 7- 13). Thus, the choice of an appropriate treatment remains controversial ( 5, 6). Despite the fact that the treatment of these fractures has been developed significantly within the recent years, best treatment has been remained difficult and challenging mainly due to severe injured soft tissue, high-energy pattern of the fracture and severe edema ( 2- 4). Pilon fracture accounts for 1% of lower extremity fractures and 5-7% of tibial fractures ( 1, 2).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
